The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
Effective price floors keep market price.
Price and quantity controls.
However price floor has some adverse effects on the market.
Price floors distort markets in a number of ways.
There are numerous strategies of the government for setting a price floor and dealing with its repercussions.
Perhaps the best known example of a price floor is the minimum wage which is based on the normative view that someone working full time ought to be able to afford a basic standard of living.
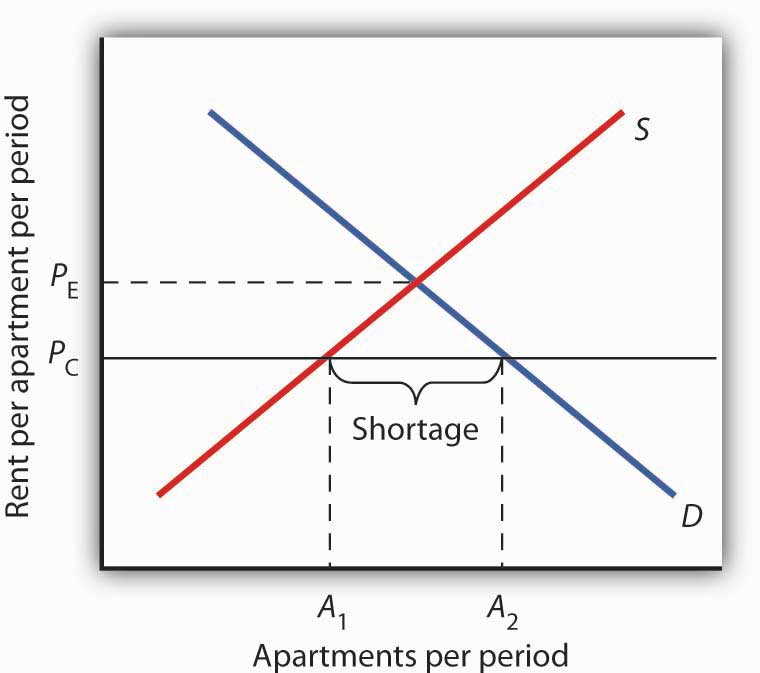
For a price floor to be effective it must be set above the equilibrium price.
Minimum wage and price floors.
For example they promote inefficiency.
The most common example of a price floor is the minimum wage.
Market interventions and deadweight loss.
Simply draw a straight horizontal line at the price floor level.
It is usually a binding price floor in the market for unskilled labor and a non binding price floor in the market for skilled labor.
Consumers will definitely lose with this kind of regulation as some people are priced out of the market and others have to pay a higher price than before.
Government set price floor when it believes that the producers are receiving unfair amount.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.
They can set a simple price floor use a price support or set production quotas.
Government enforce price floor to oblige consumer to pay certain minimum amount to the producers.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
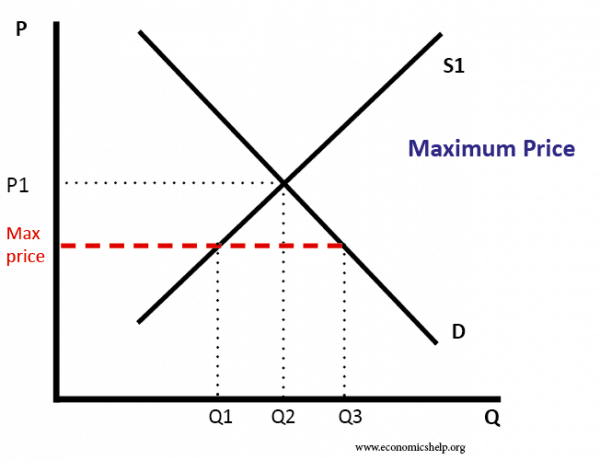
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Surplus product is just one visible effect of a price floor.
This is the currently selected item.
Some suppliers that could not compete at a lower market equilibrium price can survive and prosper at the higher government mandated price level.
For example the uk government set the price floor in the labor market for workers above the age of 25 at 7 83 per.
Price ceilings and price floors.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
In agriculture price floors have created persistent surpluses of a wide range of agricultural commodities.
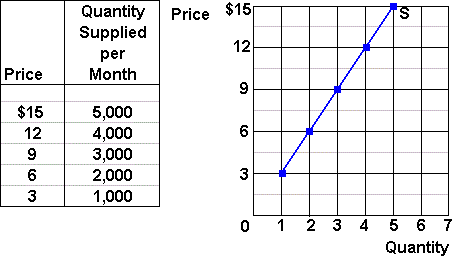
This graph shows a price floor at 3 00.
Effect of price floor.
If it s not above equilibrium then the market won t sell below equilibrium and the price floor will be irrelevant.
For a price floor to be effective the minimum price has to be higher than the equilibrium price.
At the price set by the floor the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
Drawing a price floor is simple.
The price floors are established through minimum wage laws which set a lower limit for wages.